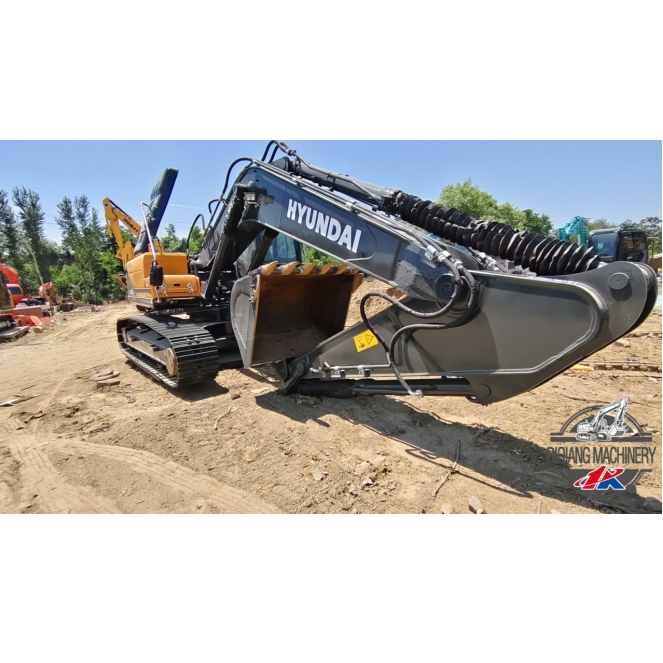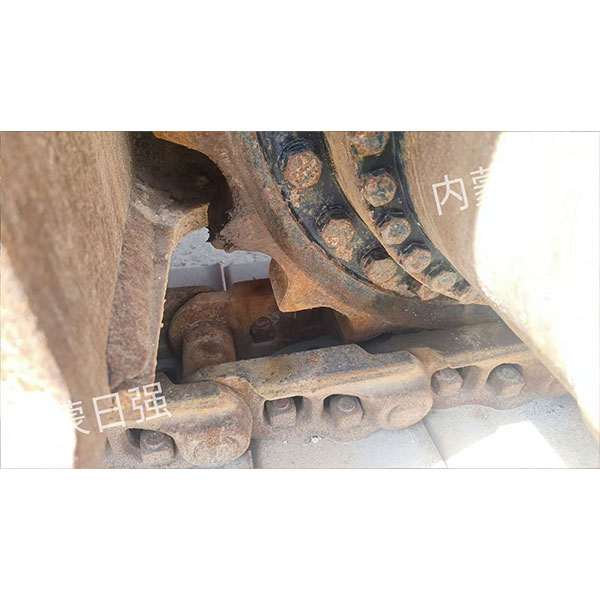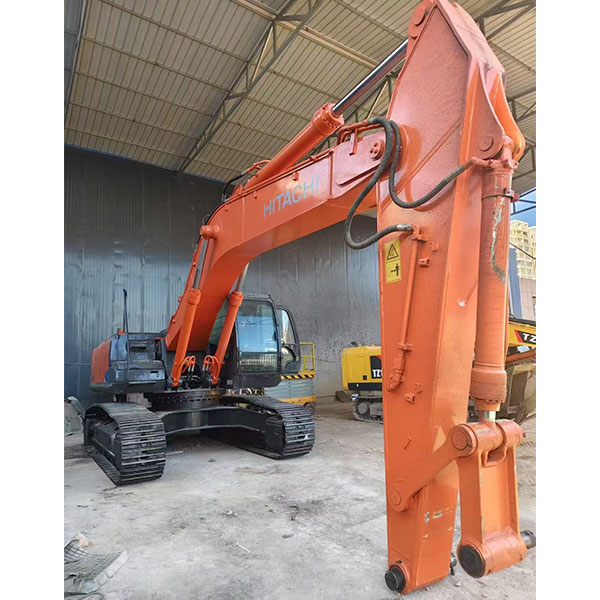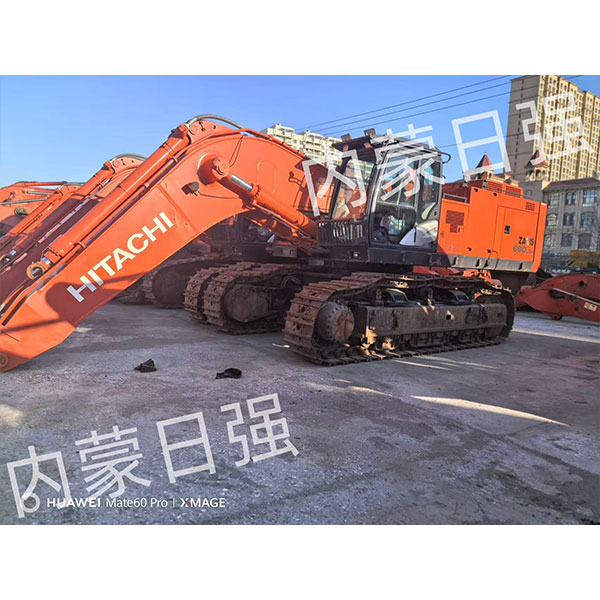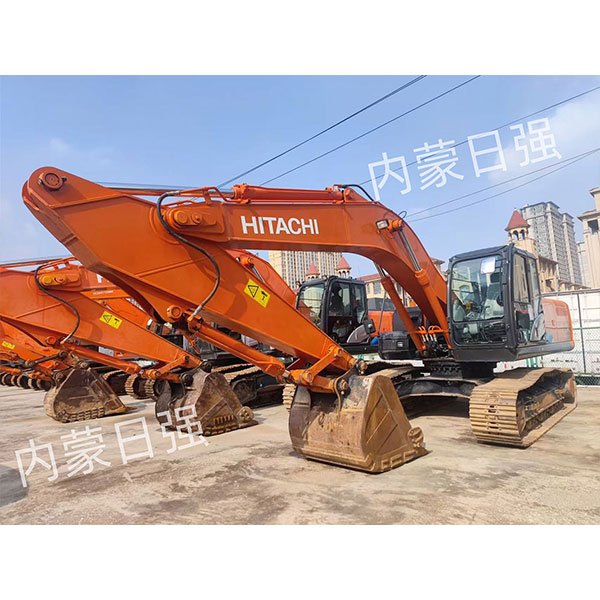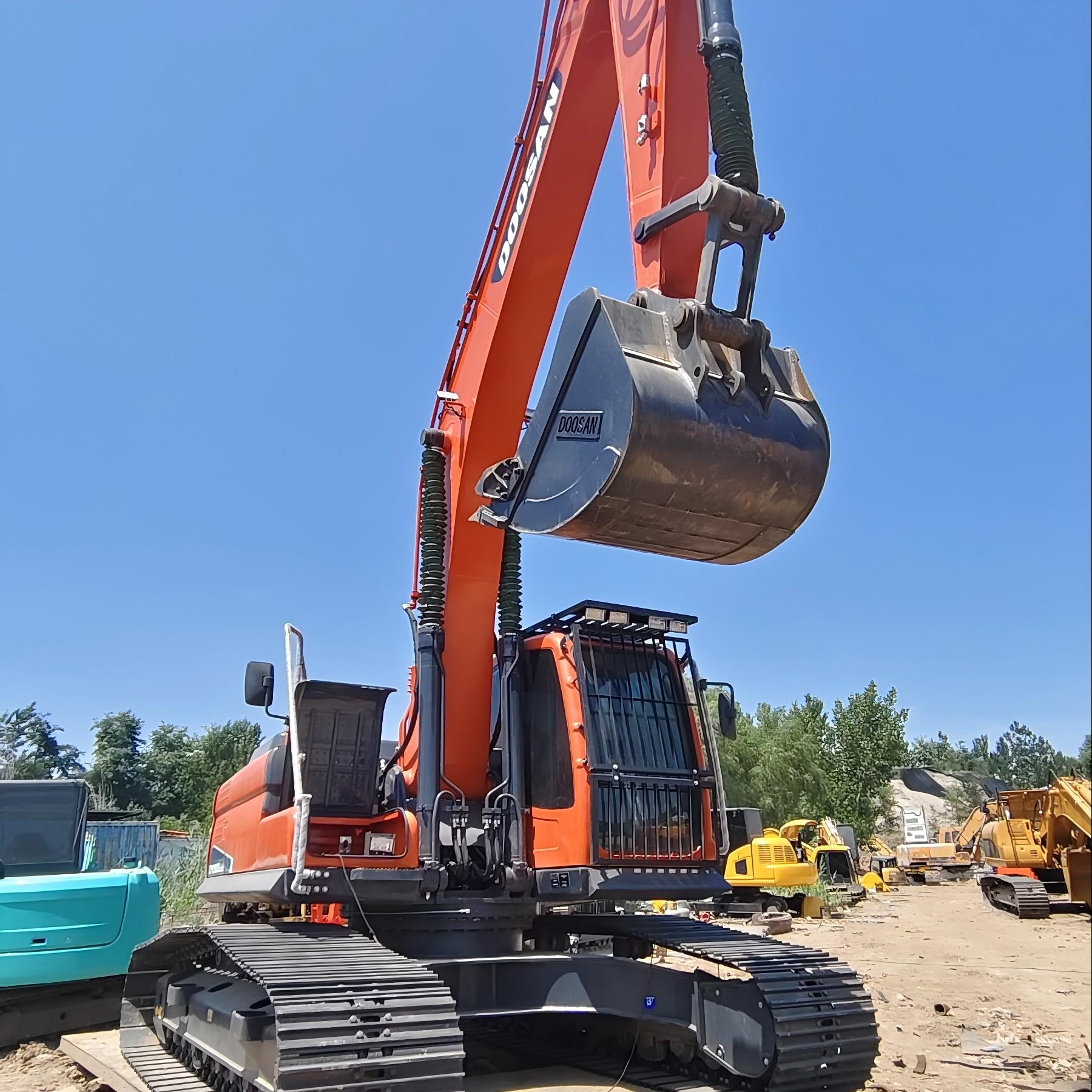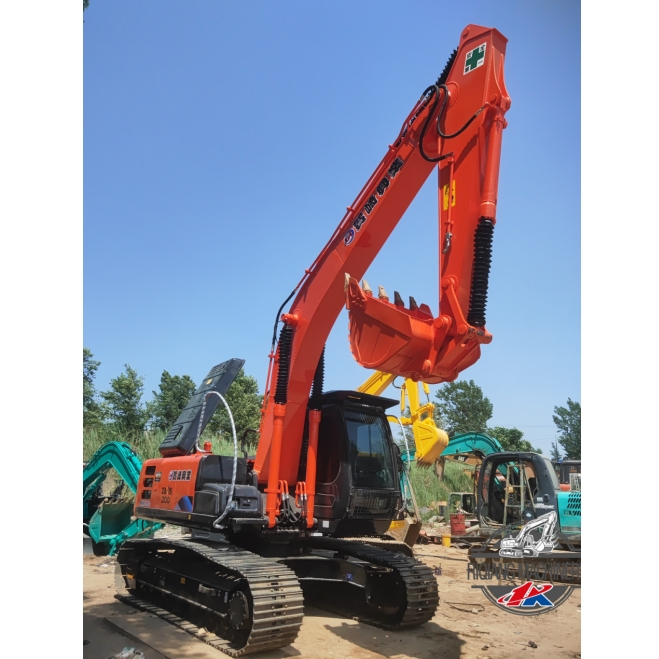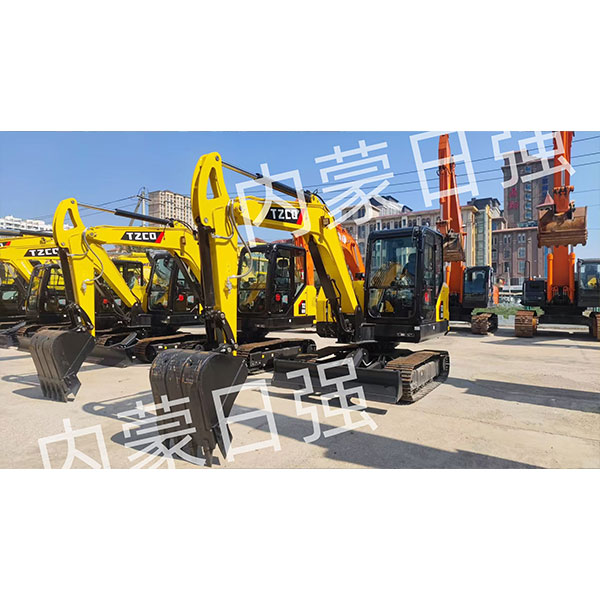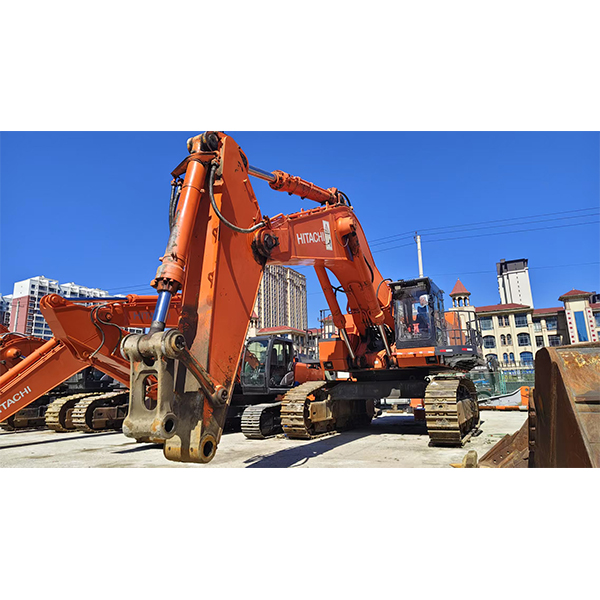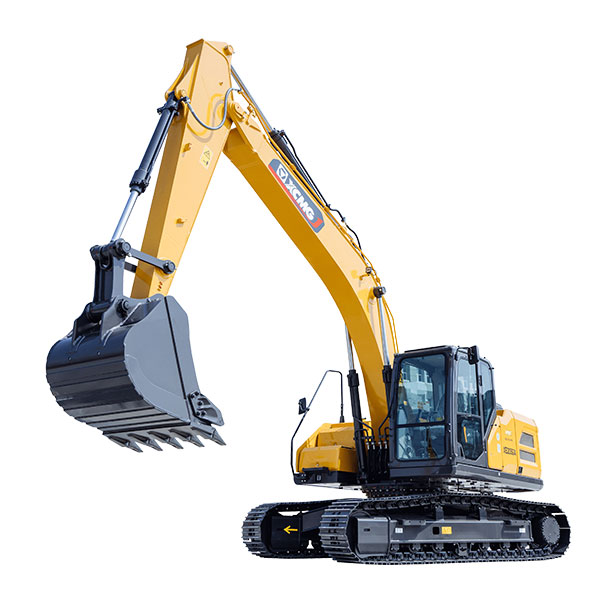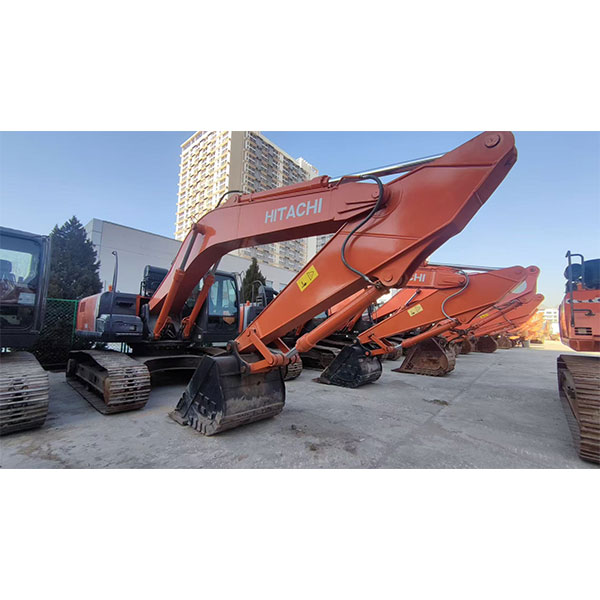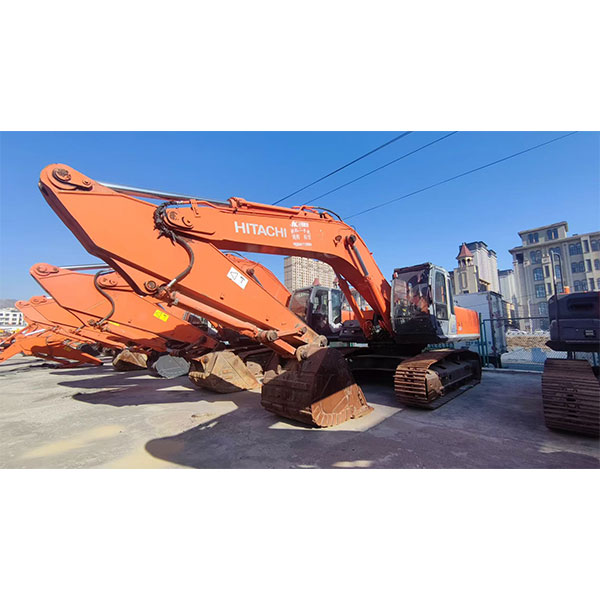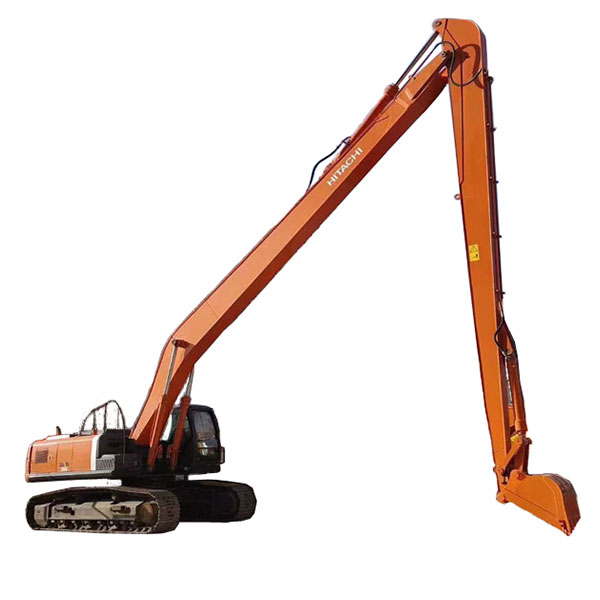
Products
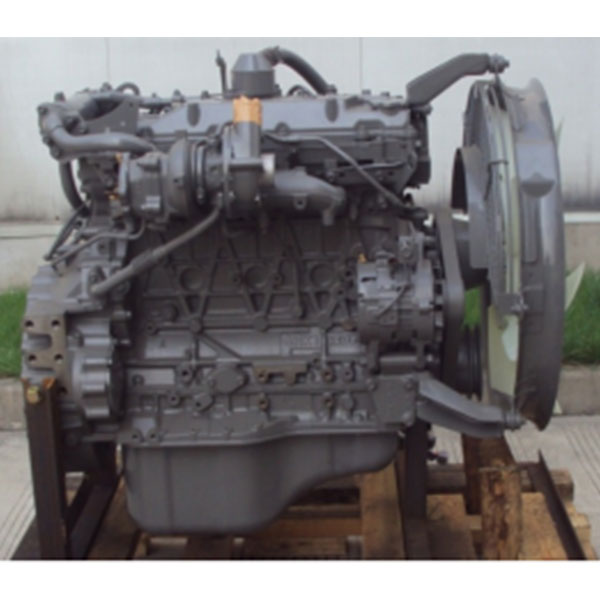
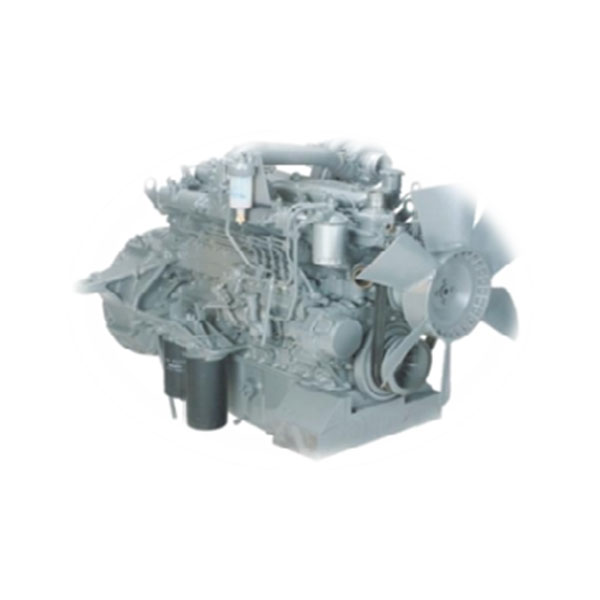
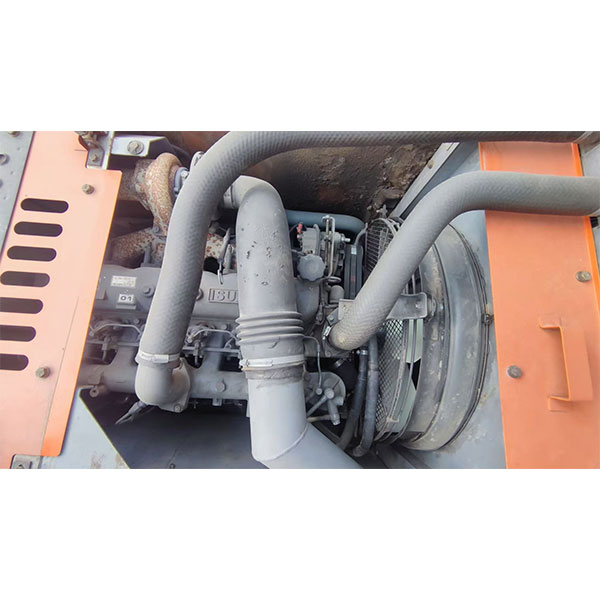
Engine details
Internal mechanical components 、 Components of the fuel supply system 、 Components of the inlet and release system
Description
marker
Introduction to the product
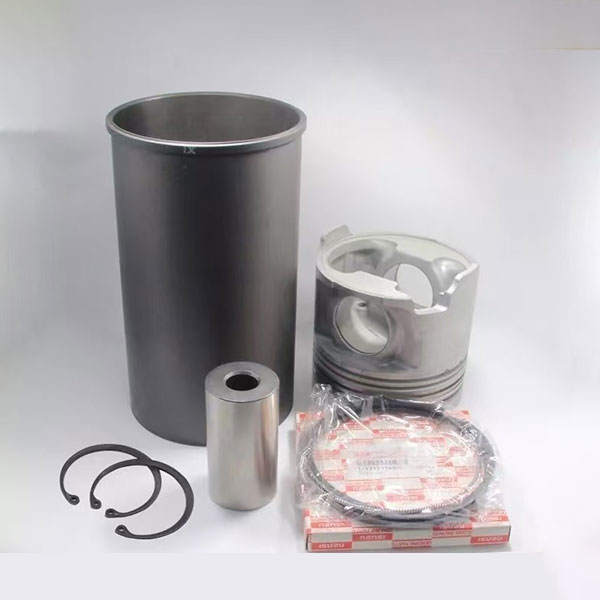
Internal mechanical components
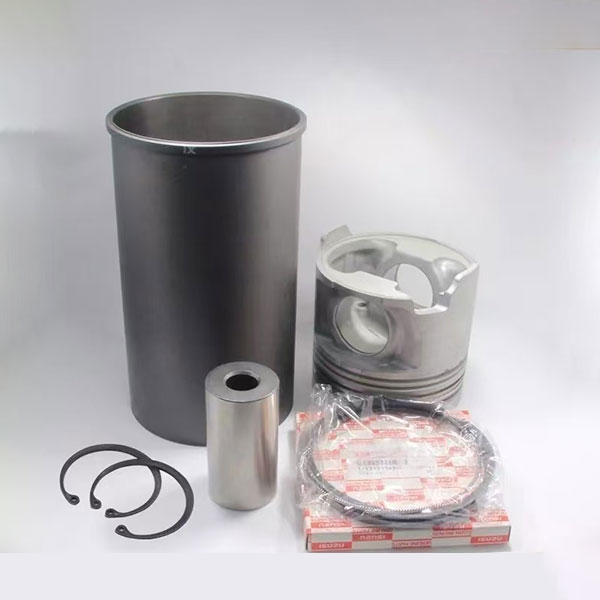
1. Four -complex set: includes a piston, piston rings, piston finger and sleeve. The piston works at high temperatures and pressure, should have high strength and wear resistance; piston rings perform the functions of sealing, controlling oil and heat -voltage; the piston finger connects the piston and connecting rod; The sleeve serves the guide for the piston, taking on the side and gas loads.
2. A crooked-shaped mechanism: converts the reciprocating movement of the piston into rotational, ensuring the transmission of power to the wheels of the car, withstands huge torque and pressure, is the key component of the engine.
3. Distribution shaft: controls the opening and closing of the valves, accurately adjusting the intake and production time in the engine, which is important for engine performance and fuel saving.

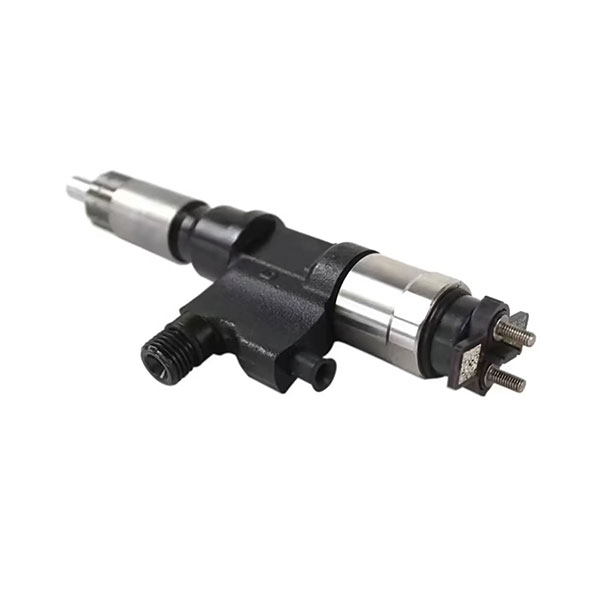
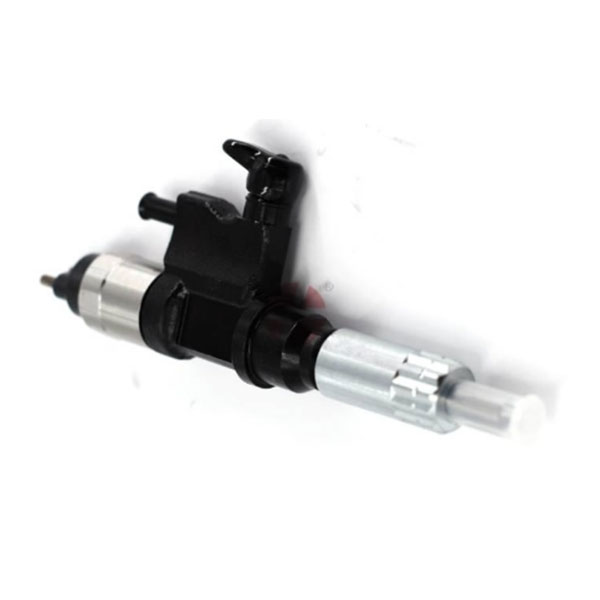
Fuel supply system components
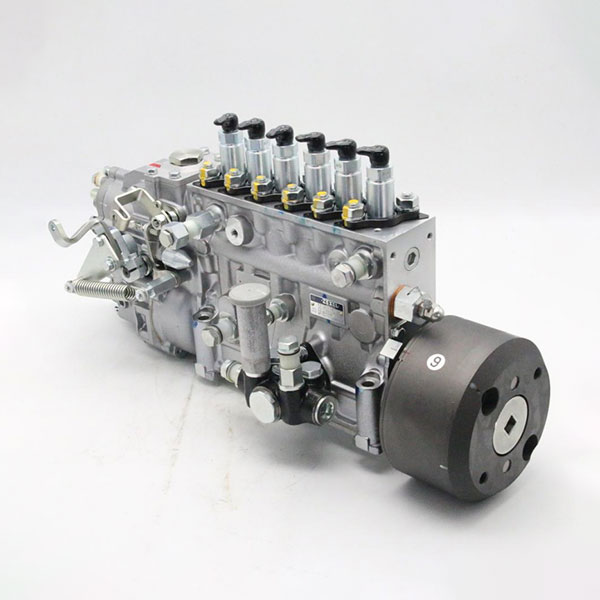
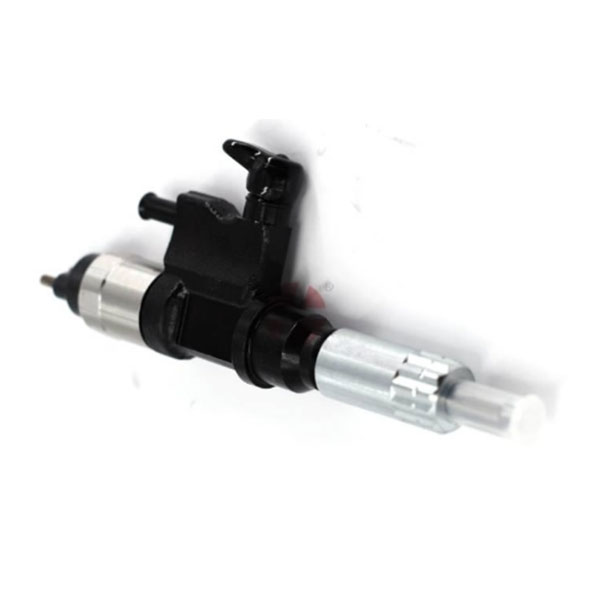
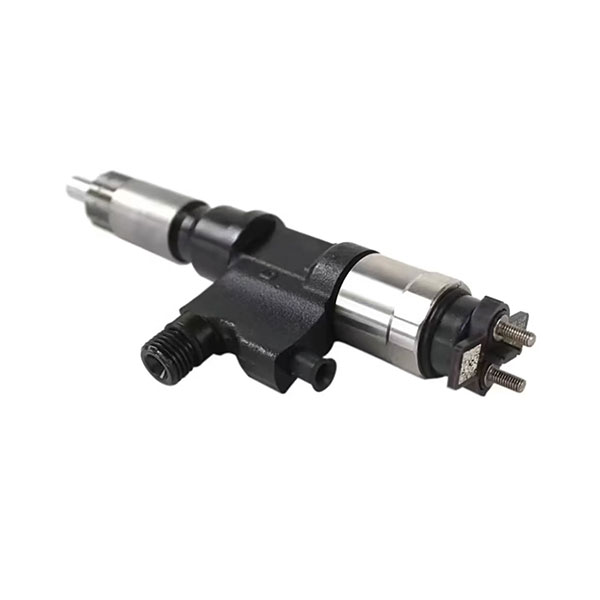
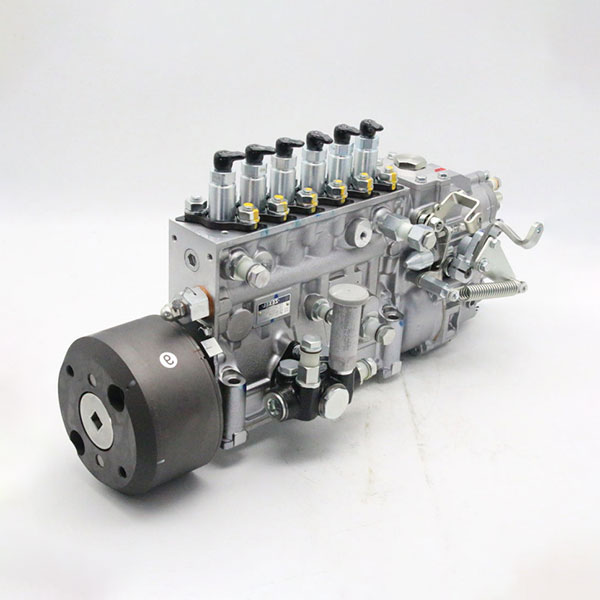
1. Fuel pump: removes diesel fuel from the tank, supplies it under pressure to the nozzles, providing high fuel pressure for injection. The stability and accuracy of its operation directly affect the power of the engine and fuel consumption.
2. Incomus: at the command of the engine control unit, the high pressure of diesel fuel in the combustion chamber sprays, creating a fine cloud, which allows the fuel to mix well with air for effective combustion. This is a key component that affects the effectiveness of combustion and emissions.


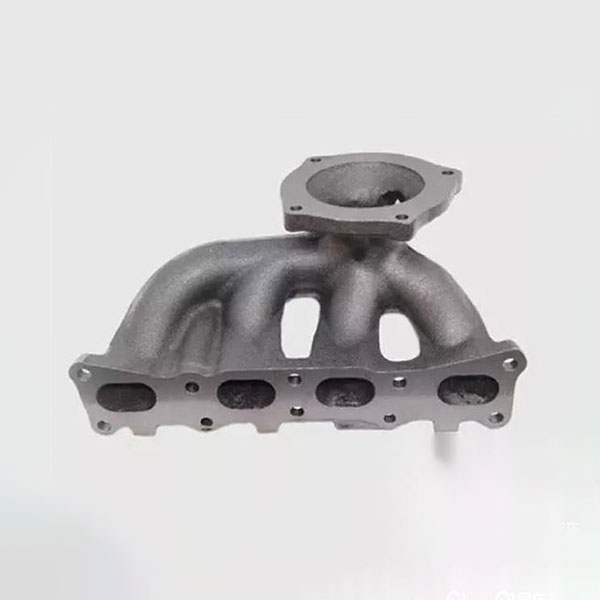
Components of the inlet and release system
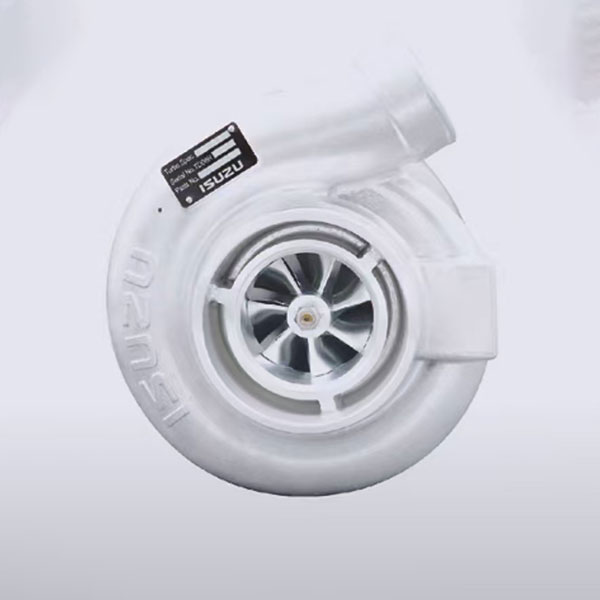
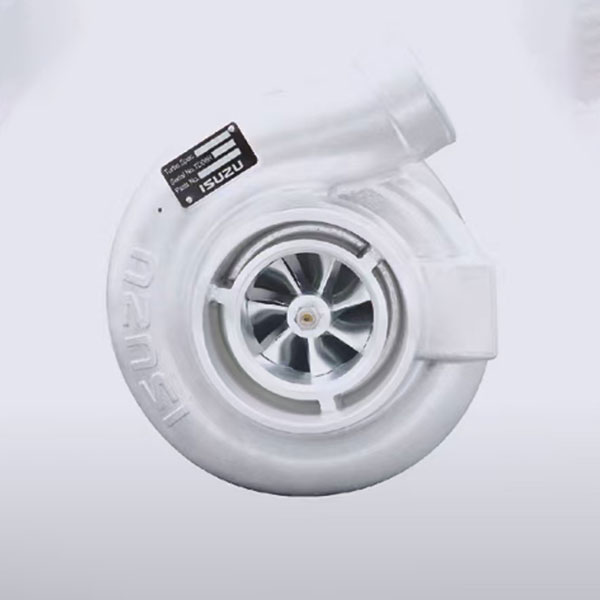
1. Turbo compressor: uses exhaust gas energy to rotate the turbine that drives the compressor to compress air, increasing the volume of air intake into the engine, which increases power and torque.
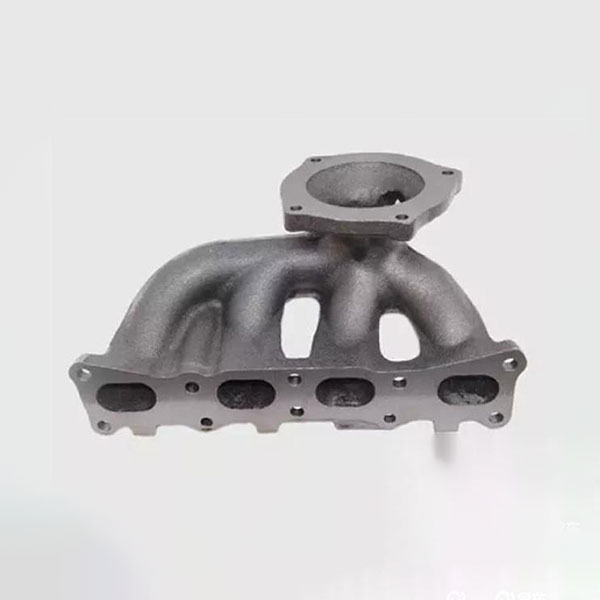
2. Collector of inlets: evenly distributes air through the cylinders, allowing the fuel and air to mix well and create a high -quality combustible mixture. Its design and manufacturing quality affect the efficiency of intake and the combustion process.


Components of the cooling and lubrication system
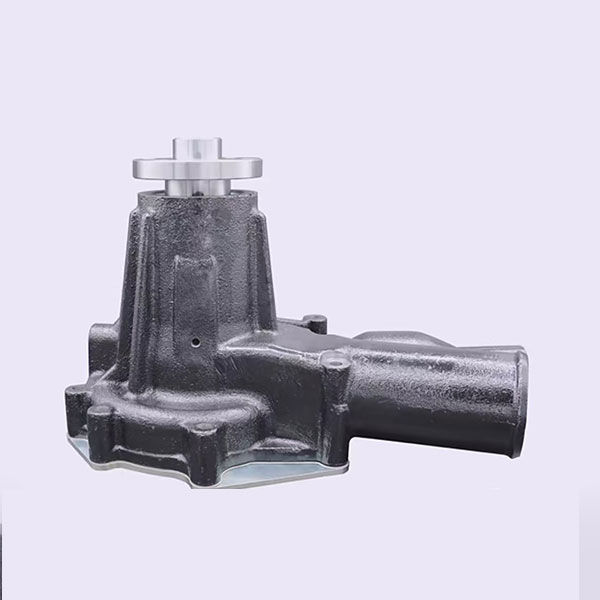
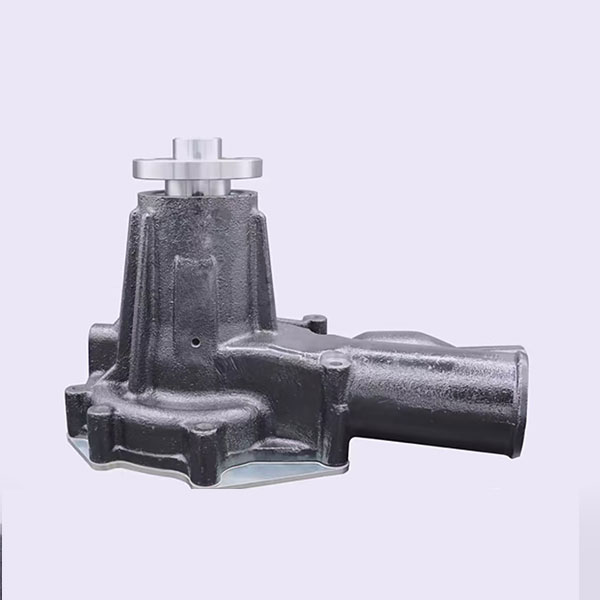
1. Water pump: The coolant circulating through the engine drives the coolant, transmitting heat from the engine to the radiator for cooling, ensuring the engine operation in normal temperature limits.
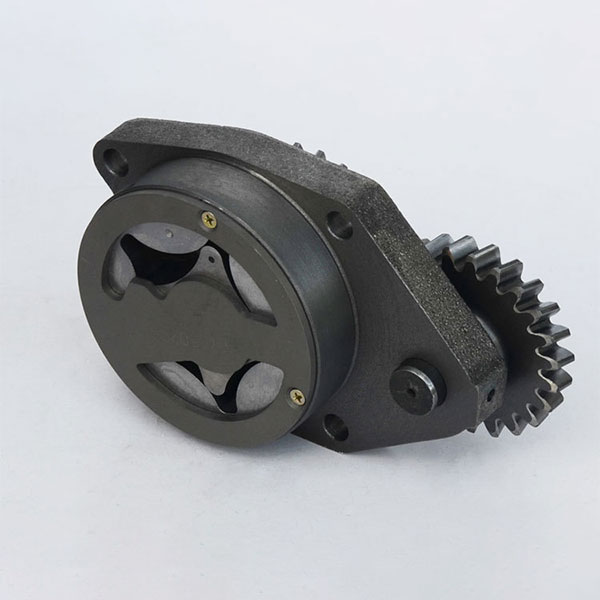
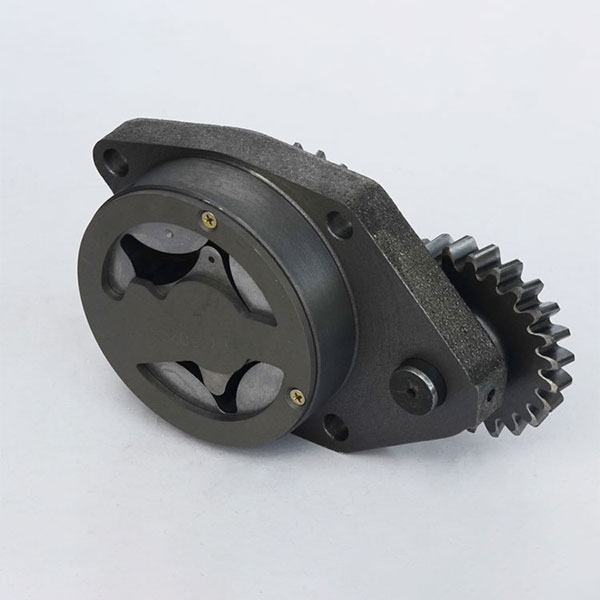
2. Oil pump: supplies oil from the crankcase, creating pressure for supplying oil to the friction surface of the moving parts of the engine, performing the functions of lubrication, cooling, cleaning and sealing. This is an important component for the normal operation of the engine.


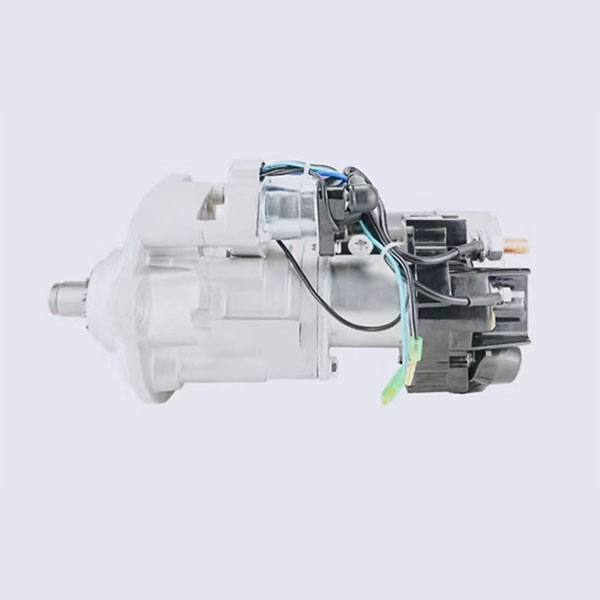
Electric components
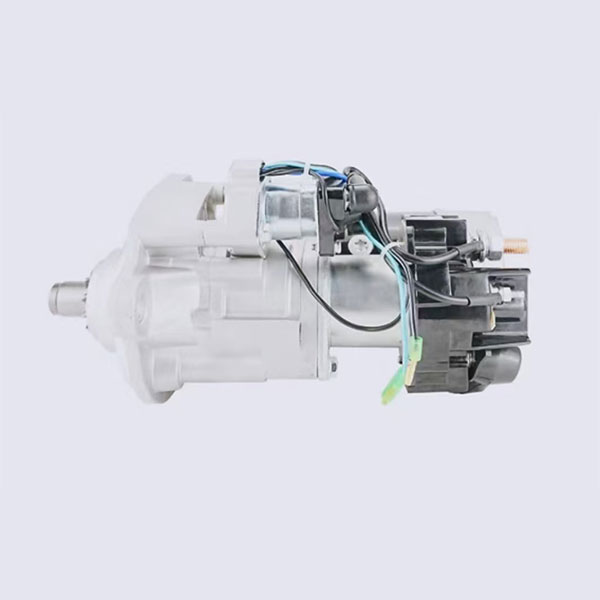
1. Starter: converts electric energy into mechanical, forcing the crankshaft of the engine to rotate to start it. It is a key component for starting the engine.
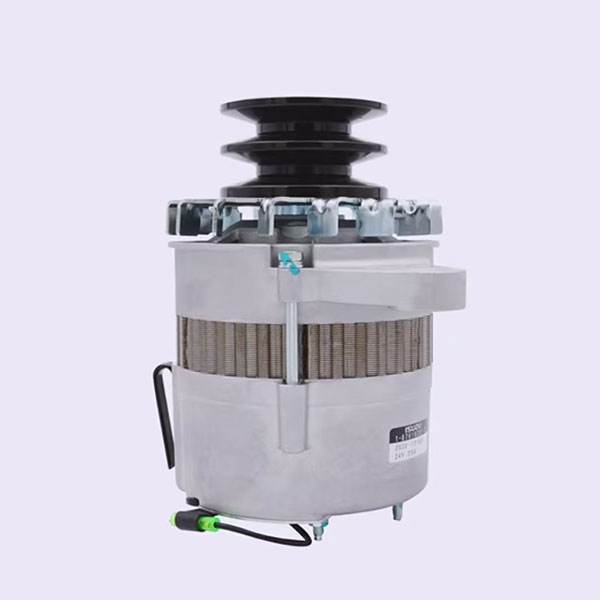
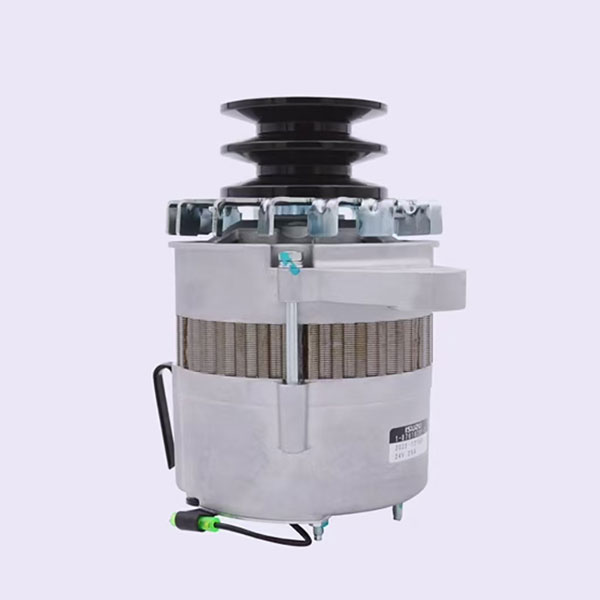
2. The generator: converts the mechanical energy of the engine into an electric one, providing charging and power supply of the electric system of the car, maintaining the normal operation of all electrical devices.